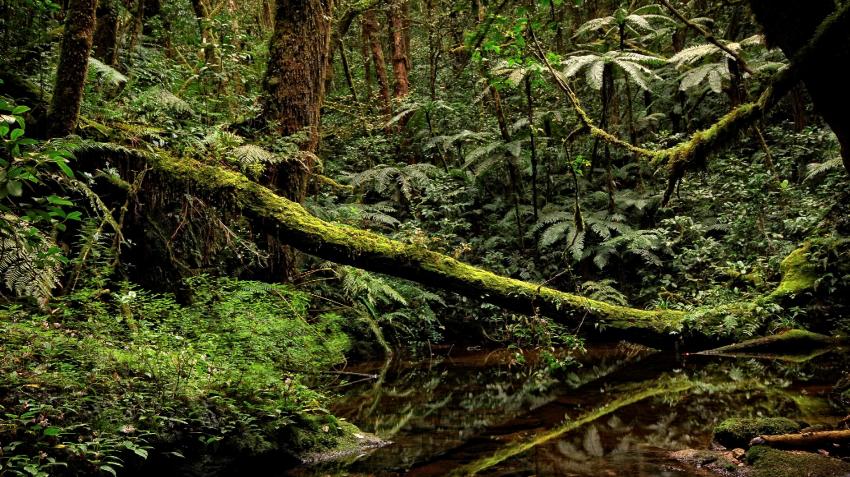
Montane Moist Forest in the Nguru mountains, central Tanzania: Photo Credit Francesco Rovero
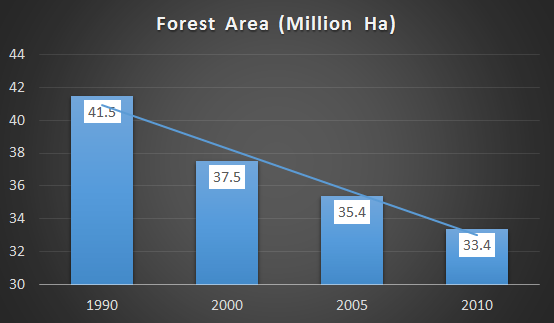
Forests in Tanzania play an important role in the daily livelihoods. They are an important source of energy for cooking, building timber, traditional medicine, tourism, fodder, water catchments, shelter for wildlife and estuaries for fish breeding areas. Furthermore, these forests also have high biodiversity, containing over 10,000 plant species, hundreds of which are nationally endemic, 724 species of flora and fauna identified as threatened in the IUCN Red List, and 276 species of flora and fauna classified as endangered (IUCN, 2013).
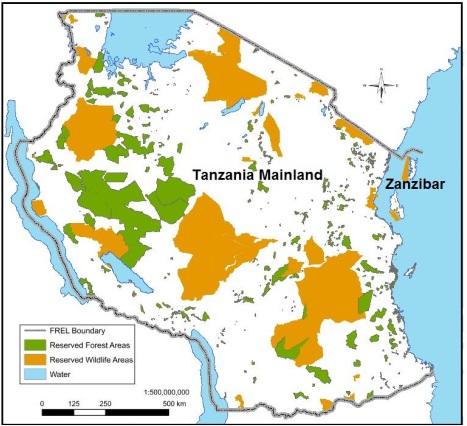
Reserved areas in Tanzania (Mainland and Zanzibar) include Conservation Areas, namely, National Parks, Game Reserves, and Nature Forest Reserves (Protective); and Forest Reserves (Protected and Production). These nature forest reserves and forest reserves are managed by either the Central Government or the Local Government Authorities. The reserved area occupies almost 50% of the forested area in Tanzania. These reserved areas are legally protected, and therefore, it is possible to reverse the current forest losses with interventions.