Cloudlands Forest taken from the summit of Chinziwa: Photo Credit BT Wursten
In Mozambique, the exploitation of forest resources is governed by the Policy and of Forests and Wildlife Development Strategy, Forestry and Wildlife Law 10/99 and its Regulation approved by Decree 12/2002 of June 6, which resulted from a participatory process. The forests in Mozambique are managed by National Directorate of Forestry in the ministry of Ministry of Land, Environment and Rural Development (MITADER).
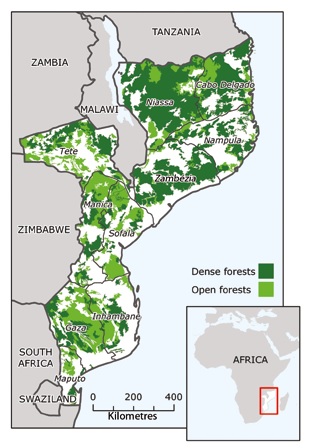
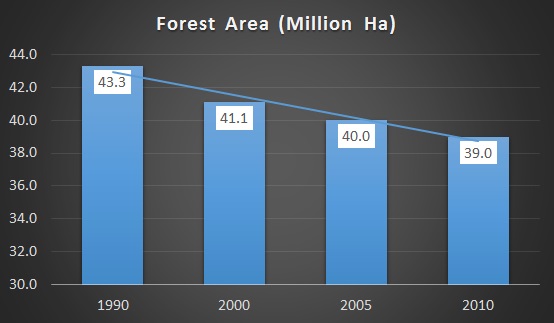
Mozambique still has a large forest cover with forests of different densities and composition, occupying an area equivalent to 70% of the total area of the country and the commercial value being exploited at a level of about 515.7 to 640.5 thousand m3 per year. The area covered with forests is estimated at 40.1 million hectares (51%), of which 26.9 million are suitable for the production of commercially valuable timber, and 13.2 million hectares are conservation areas. The country Global Forest Resources Assessment was conducted in 2010 (FRA 2010).
Unknown Mozambique Forest Found Through Google Earth
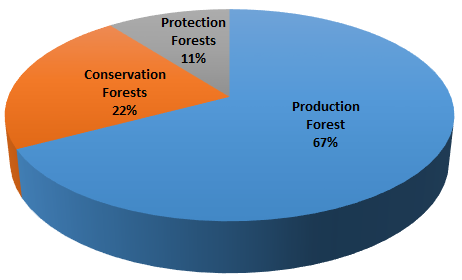
As the main custodian and owner of all national forests, the government manages and allocates forests to other stakeholders. Local communities can lease portions of the forest estate if they are registered according to the laws. Forests in Mozambique are divided into three types of forests: conservation forests, production forests and protection forests.
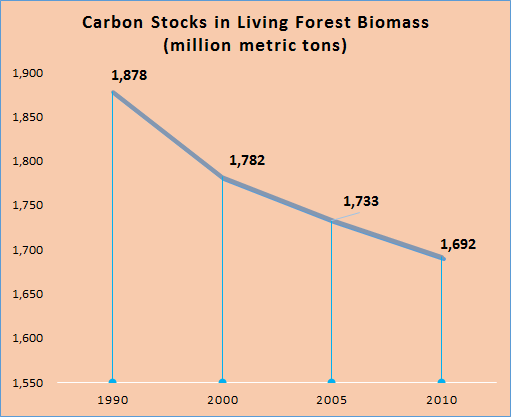
The country has ongoing programmes that contribute to Establishment of a REDD+ system in Mozambique, these include; developing a forest resource information platform, developing an infrastructure for measurement, reporting, and verification (MRV) using that platform, forming Reference Emissions Levels or Reference Levels (REL/RL) for deforestation and forest degradation, and development data sets for estimation of forest biomass and carbon volumes. Also the country is implementing regular and appropriate monitoring systems of forest resources. Other ongoing country activities include; developing National Forestry strategy, National Forest Safeguards; study in drivers of deforestation and degradation, and Strategic Environmental and Social Assessment (SESA) under REDD+.
MITADER has adopted several strategic actions to address challenges in the forest sector including; a participatory audit of all forest concessions, the suspension of new requests for exploration areas, a ban on log exports, the updating of forest policies and regulations, and an ambitious project called “Floresta em Pé”, which aims to promote sustainable integrated rural development though protection, conservation, valorization, creation and sustainable management of forests.